EXARC Journal - Latest Articles
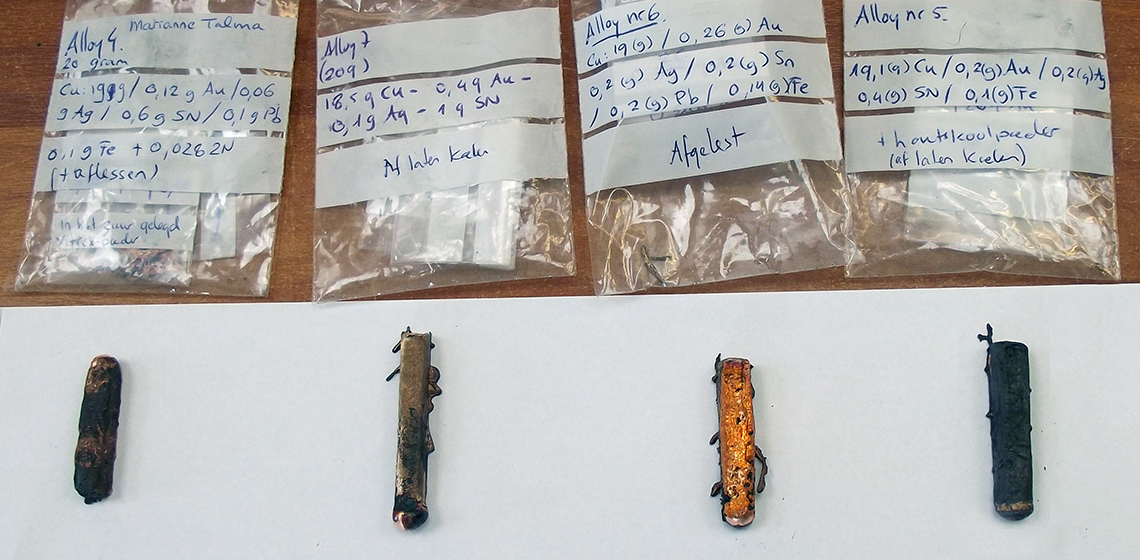
An Experimental Diachronic Exploration of Patination Methodology of Dark Patinated (Arsenical) Copper Alloys on Case Studies from the Eastern Mediterranean Bronze Age and Early Iron Age
Artificially dark patinated copper alloys appear in various times and regions and are commonly applied in prestigious polychrome metallic objects. Currently, the earliest finds known are from ca. 2000 BC in Egypt (See Fig. 1) and Palestine (See Fig. 2), followed by ca. 1500 BC in Greece and Cyprus (See Fig. 3 and 4) and again during the Roman period from ca. the late 4th century BC (See Fig. 5 and 6).
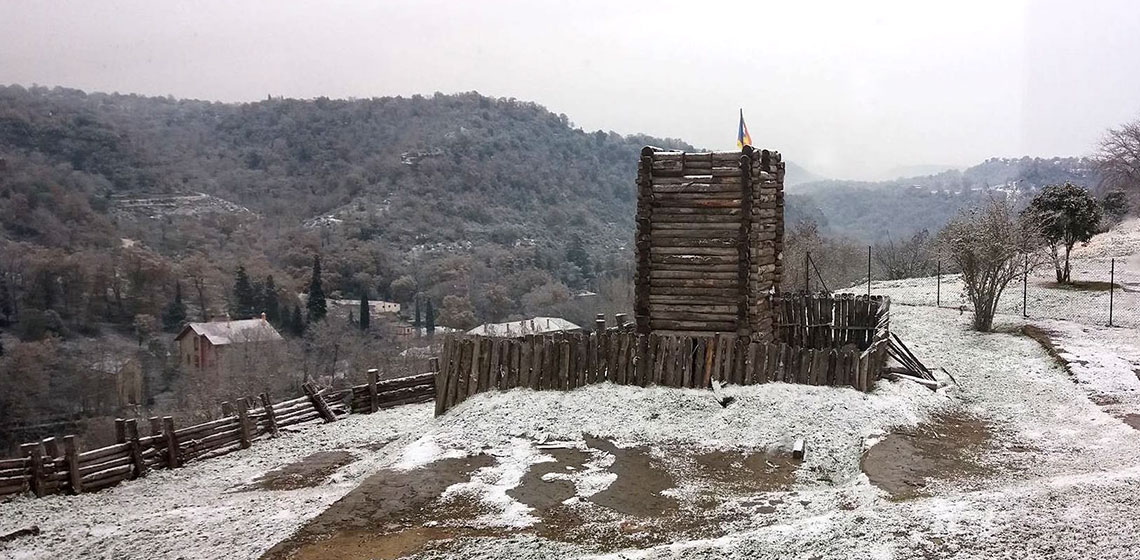
The Experimental Building of a Wooden Watchtower in the Carolingian Southern Frontier
***During fifteen days of June 2015, the team of l’Esquerda worked in a research project to build a Carolingian wooden watchtower on the River Ter, in Roda de Ter, Catalonia, Spain. The idea was to test our hypotheses experimentally, (a) if the wooden watchtower could...
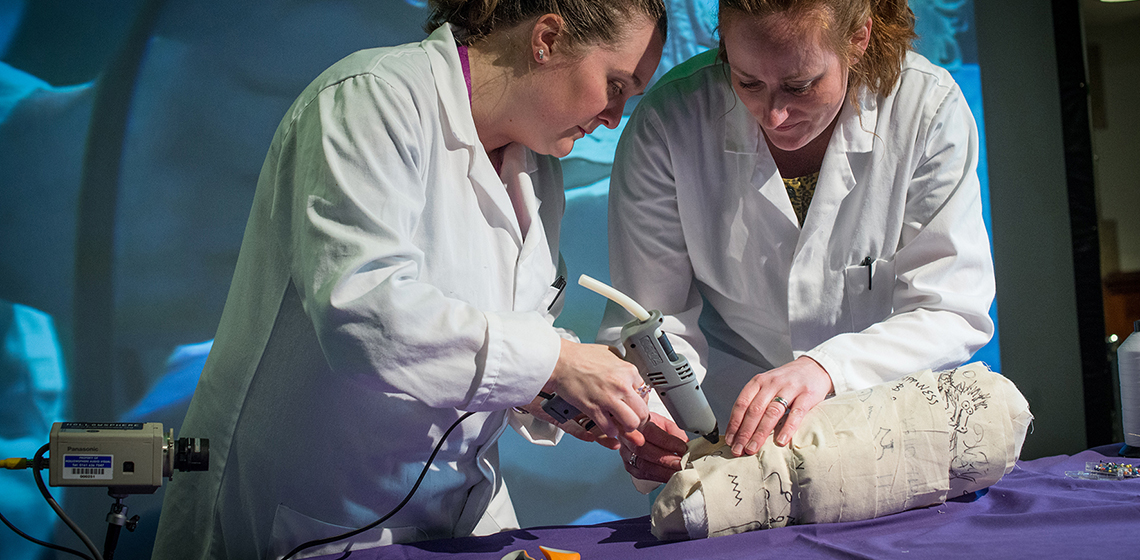
‘Re-rolling’ a Mummy: an Experimental Spectacle at Manchester Museum
Introduction
The unwrapping and dissection of mummified bodies was a common practice in 19th century Europe. These autopsies were conducted as part of scientific endeavours and social spectacles, motivated by a desire to advance the fields of science, medicine and archaeology, coupled with a sense of macabre fascination (Moshenska, 2014). The scientific capability required to study mummified remains non-invasively had yet to be developed, leading to the destruction of many hundreds of specimens.
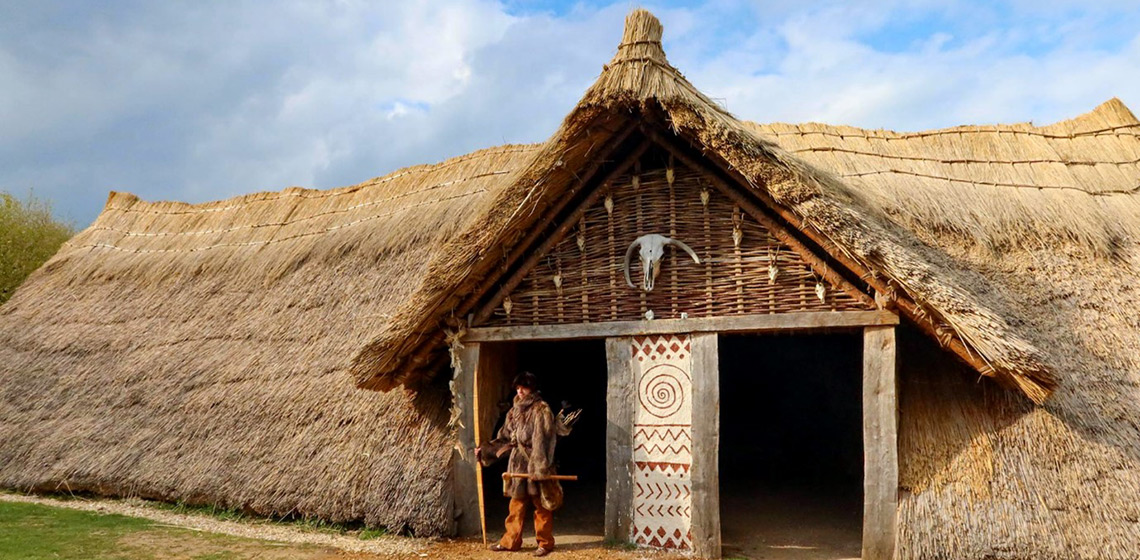
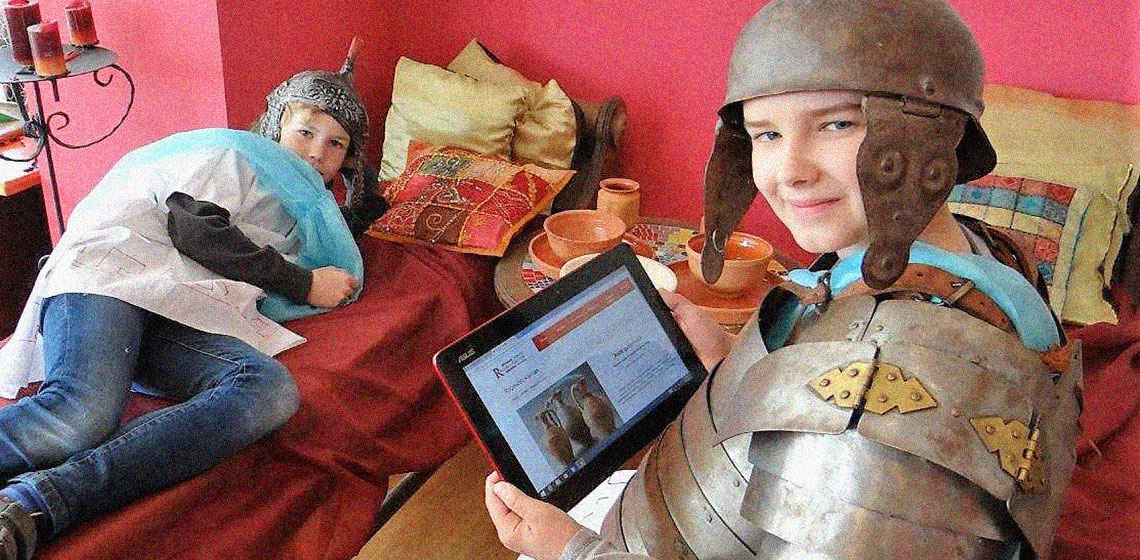
Vacation in the Past - Effective Heritage Interpretation through Education
***Heritage sites are breathing memories from the past; however, visitors can hardly imagine or experience the ancient life on the spot. In fact, these visits are supposed to conjure up journeys back into the past and park managers should facilitate such experiences by the most effective means possible in order to help tourists gain...
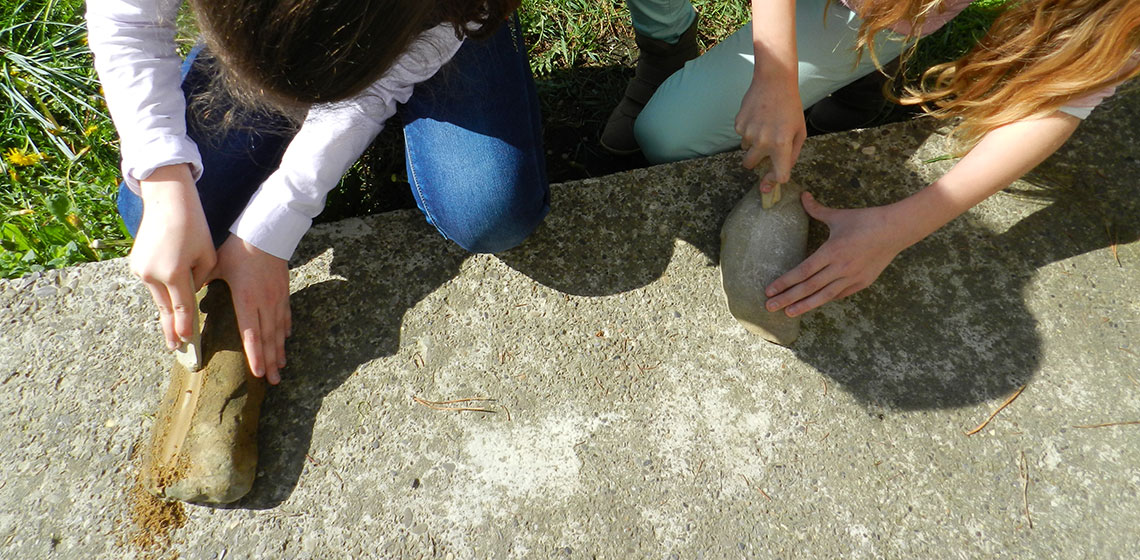
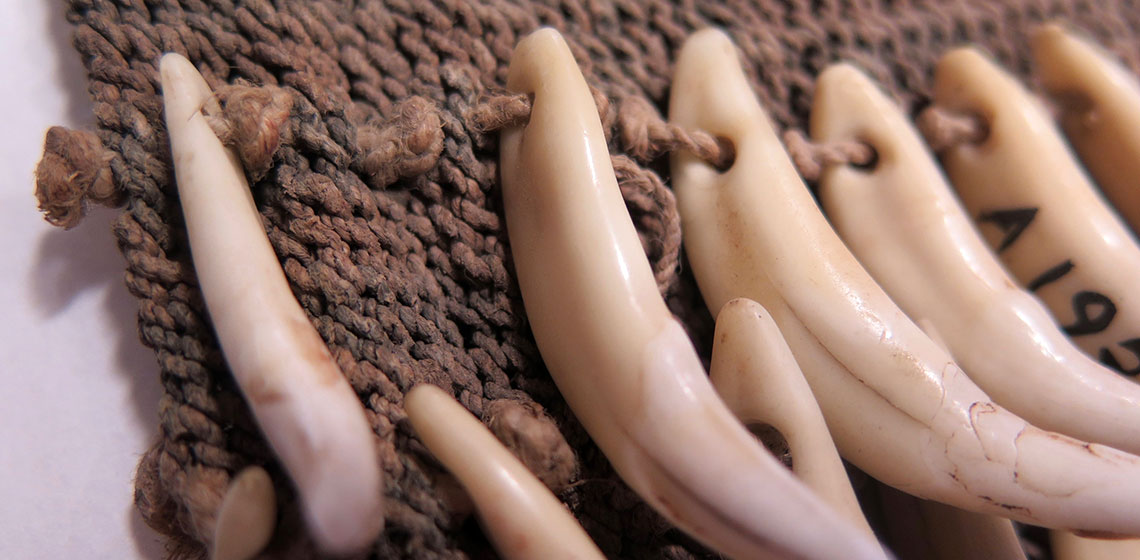
Animal Teeth in a Late Mesolithic Woman’s Grave, Reconstructed as a Rattling Ornament on a Baby Pouch
***In one of the Late Mesolithic graves at Skateholm, Sweden, dating from 5500–4800 BC, was buried a woman together with a newborn baby. Altogether 32 perforated wild boar (Sus scrofa) teeth, along with traces of red ochre pigment, were found in this grave. We interpreted these artefacts as a rattling ornament decorating a baby pouch...

 The EXARC Journal (since 2004) is the leading Journal for those involved in
The EXARC Journal (since 2004) is the leading Journal for those involved in