education
The Best Way of Preserving Something is to Educate about it - Educational Centres in South Africa
Publication Date
This article aims to show the kind of issues South- African archaeologists have, working with public archaeology. A past that was segregated earlier should now be shared, but sharing a common past includes alternative perspectives on history and archaeology, for the archaeologist as well as for the public.
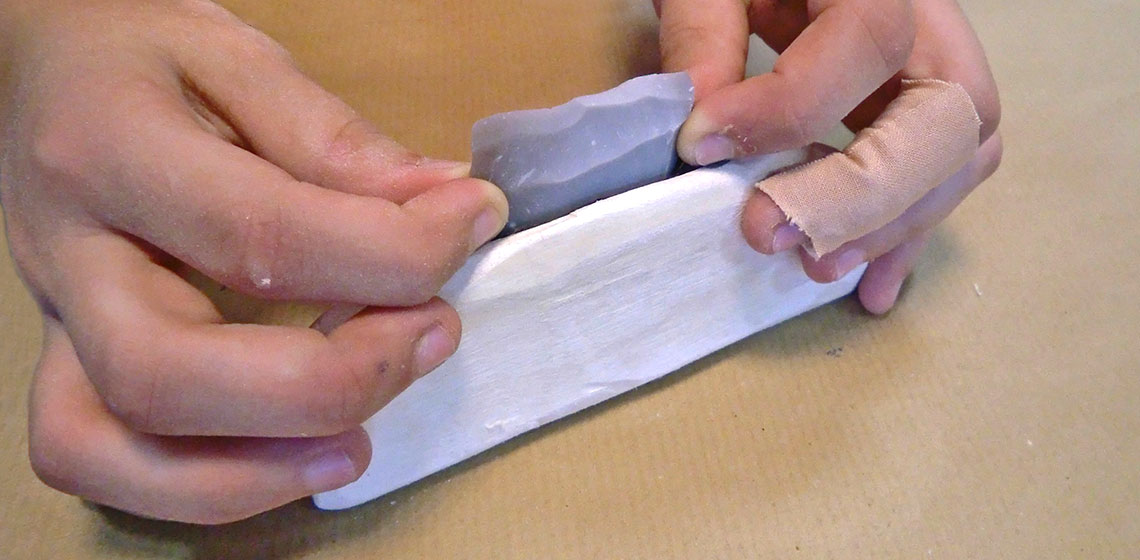
Discussion: Working with Knives in Archaeological Open-Air Museums
Publication Date
This is an extract from a lengthy and lively Facebook discussion in the Archaeological Open Air Museums group, started on the 5th of February 2016 by Roeland Paardekooper, at that time in the...
Playing with the Past? Or Saving Our Future?
Publication Date
As the manager of the Ancient Technology Centre (ATC) in Dorset, England, like many of you, I consider regularly what it is that we actually do. What services do we provide? How are we regarded by the public, by the education sector, by the children we teach, and by those who pay to come through our doors.
Event Review: Daily Life and Feasting in the Neolithic: Celebrating the Tenth Anniversary of Experience in Experimental Archaeology at the Steinzeitdorf Albersdorf
Publication Date
OpenArch Special Digest 2015 Issue 2
***During summer 2014, just over 30 students from Archaeological Studies at the University of Hamburg, as well as four children, participated in a practical week of experimental archaeology at the Steinzeitdorf Albersdorf. In preparation for this week, the students attended a seminar at the University of Hamburg...
***During summer 2014, just over 30 students from Archaeological Studies at the University of Hamburg, as well as four children, participated in a practical week of experimental archaeology at the Steinzeitdorf Albersdorf. In preparation for this week, the students attended a seminar at the University of Hamburg...
What Does Your Visitor Experience? Making the Most of Live Interpretation in a Unique Setting
Publication Date
OpenArch Special Digest 2015 Issue 2
***Archaeological Open-Air Museums (AOAM) offer a unique setting in which live interpretation can make history come truly alive. For many, or perhaps all, AOAM history is the product being sold to the public. During the five years the OpenArch project has run the partners have spent many hours discussing the...
***Archaeological Open-Air Museums (AOAM) offer a unique setting in which live interpretation can make history come truly alive. For many, or perhaps all, AOAM history is the product being sold to the public. During the five years the OpenArch project has run the partners have spent many hours discussing the...
Museum Theatre in Greece: Perspectives in Site Interpretation
Publication Date
The paper summarizes preliminary findings of a research project on the use of museum theatre in Greek open-air sites, as a part of a PhD thesis. The research focuses on the exploration of the development, use and function of museum theatre in Greek open-air sites based on available secondary resources and primary research, which included site visits, interviews and data analysis...
The Steinzeitpark Dithmarschen (DE): Concept and Development of a Visitor Oriented Educational Centre for Sustainable Development
Publication Date
OpenArch Special Digest 2015 Issue 2
***What does a Stone Age village or Stone Age house look like? (Almost) every person that we happen to randomly meet can answer this question with (subjectively recognized) certainty. Since the research of the 19th century, the knowledge people assume to have is based, not lastly, on images or...
***What does a Stone Age village or Stone Age house look like? (Almost) every person that we happen to randomly meet can answer this question with (subjectively recognized) certainty. Since the research of the 19th century, the knowledge people assume to have is based, not lastly, on images or...
Book Review: Prehistory Hands-On by C. Henderson
Publication Date
Celtic Harmony is an Iron Age-like village and education centre north of London, providing natural & cultural heritage education. Hands-on activities and events based on Britain's Celtic culture promote a more sustainable way of life in harmony with the natural world...
“You could See it [the Past] in your Mind”: What Impact might Living History Performance Have on the Historical Consciousness of Young People?
Publication Date
Combining theoretical perspectives with two case studies carried out in 2008 with British students aged from 10-17 years old, this paper will explore how living history might contribute to the development of young people’s historical consciousness and help them to cope with the social and cultural differences which confront them when learning about the past. In particular, it will focus on the effectiveness of first- and third-person interpretation.
120 Years of Strategies and Experiences in Educational and Handicraft Skills
Publication Date
OpenArch Dialogue with Skills Issue
***One aim of the five year EU-funded Culture Project OpenArch is to encourage cooperation between archaeological open-air museums in Europe and ethnological open-air museums who have a long history of presenting and handicraft to the public in practical ways...
***One aim of the five year EU-funded Culture Project OpenArch is to encourage cooperation between archaeological open-air museums in Europe and ethnological open-air museums who have a long history of presenting and handicraft to the public in practical ways...