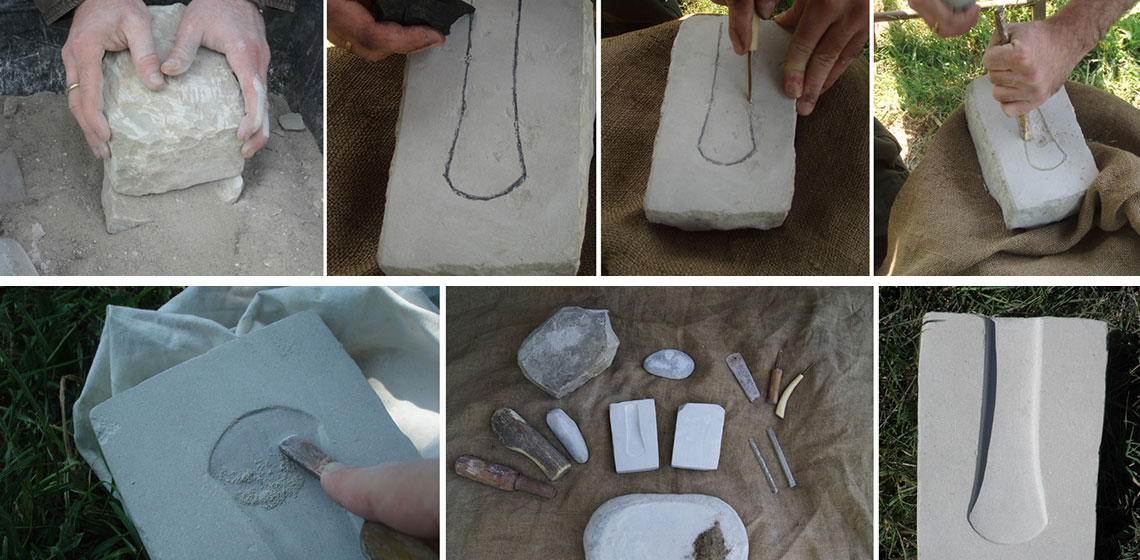
weapon
“A Mirror for Men” – Reconstructing a Medieval Polishing Bench and Putting it to the Test
Publication Date
11th EAC Trento 2019
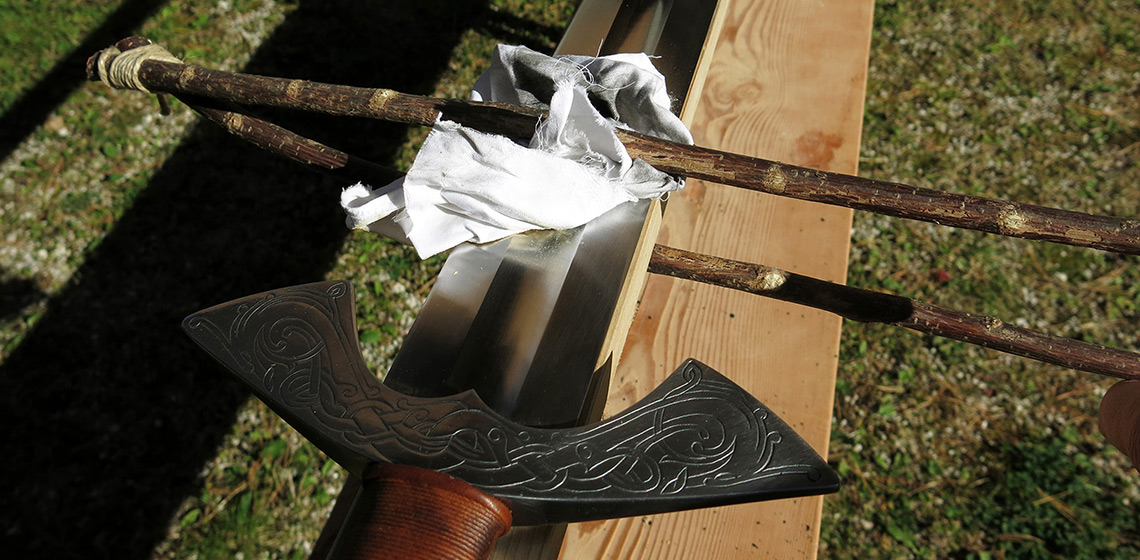
***In the late 5th century AD, the famous Ostrogoth Theoderic the Great received a truly regal gift from the king of the Warini: he was given highly elaborated swords, richly decorated and able to cut through armour. Their fullers (long grooves along the flat side of the blade to reduce weight and to gain stability...
***In the late 5th century AD, the famous Ostrogoth Theoderic the Great received a truly regal gift from the king of the Warini: he was given highly elaborated swords, richly decorated and able to cut through armour. Their fullers (long grooves along the flat side of the blade to reduce weight and to gain stability...
The Arrowheads of the Squared-Mouthed-Pottery Culture: Reconstruction and Shooting Experiment
Publication Date
11th EAC Trento 2019
***This international experimental project focused on the production of replicas of different models of flat-retouched flint arrowheads (stemmed, with flat base, and ogives -with rounded base-) in use within the Neolithic Squared-Mouthed-Pottery Culture (SMP) of Northern Italy. The aim was to test their efficiency in order to understand if...
***This international experimental project focused on the production of replicas of different models of flat-retouched flint arrowheads (stemmed, with flat base, and ogives -with rounded base-) in use within the Neolithic Squared-Mouthed-Pottery Culture (SMP) of Northern Italy. The aim was to test their efficiency in order to understand if...
The Iron Age Shepherd Sling
Publication Date
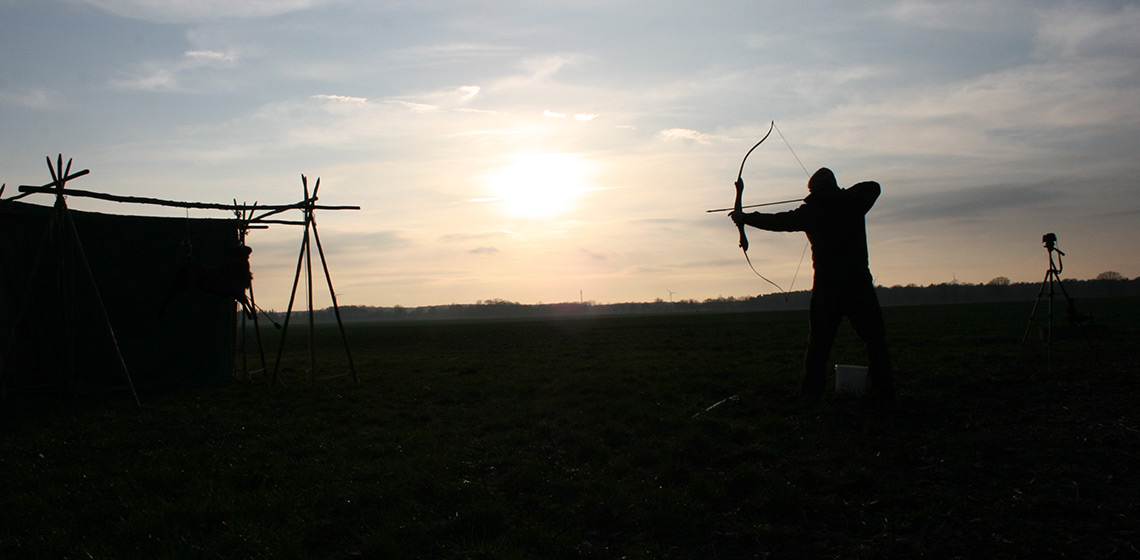
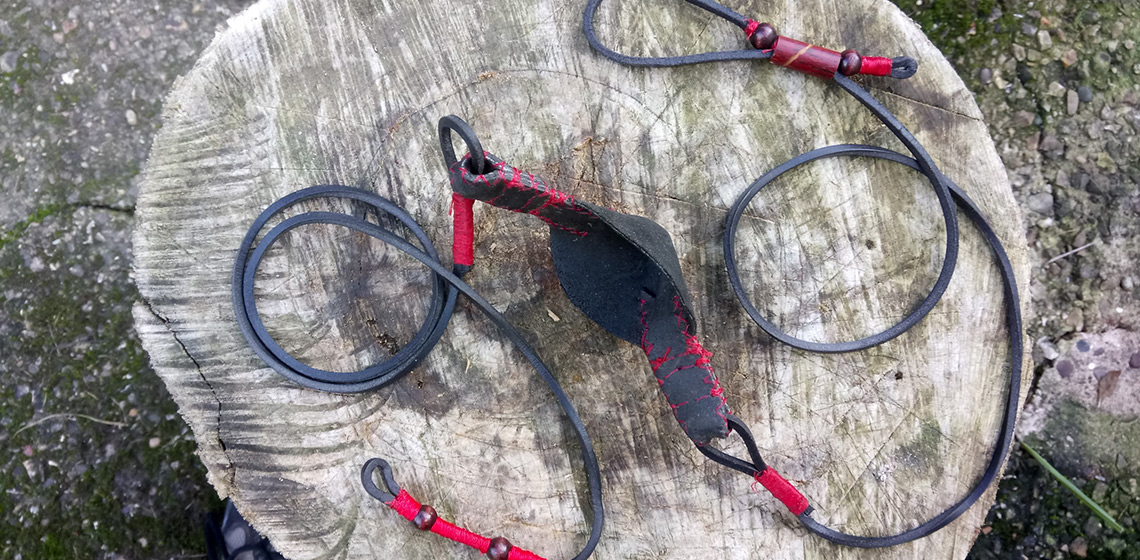
The purpose of this experiment was to examine the shepherd sling to form an understanding as to why it would appear to be the most dominant missile weapon of Iron Age Britain (Harding, 2012, p.194). The experiment consisted of making and using the sling, testing its range and accuracy to reveal its strengths and limitations. This experiment was also intended to introduce a different interpretation...
Shooting Experiments with Early Medieval Arrowheads
Publication Date
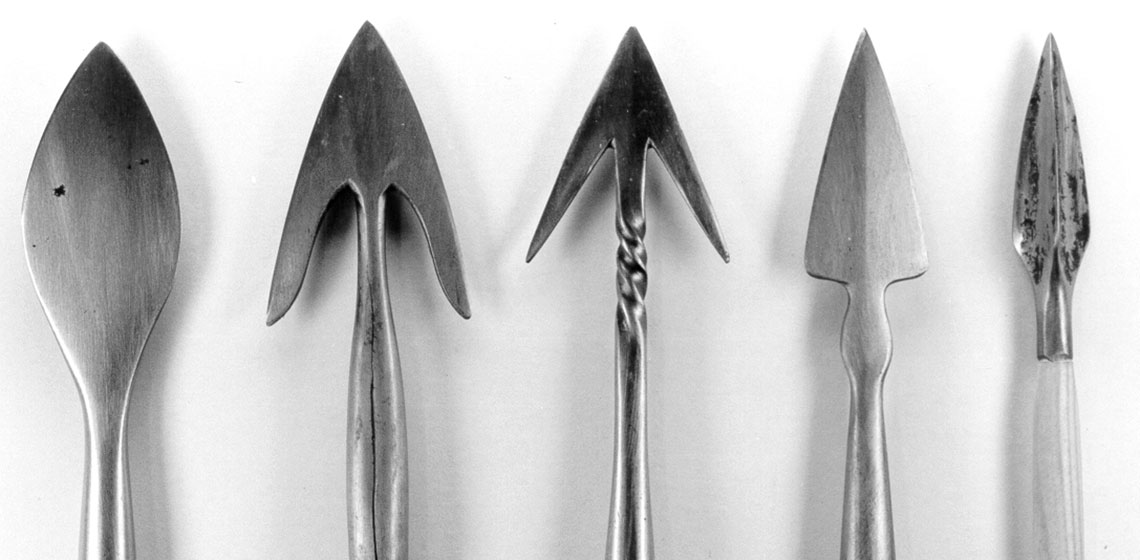
In the Merovingian era (5th-8th century AD) a lot of variously shaped iron arrowheads were used by the Franks, Alemannians and Bavarians, who dwelled in the region known today as Germany, Austria and Switzerland. As archaeological artefacts, two-winged arrowheads with rhombic, willow-leaf or triangular blades represent a standard Germanic type. Iron bodkin and needle-shaped tips are also...
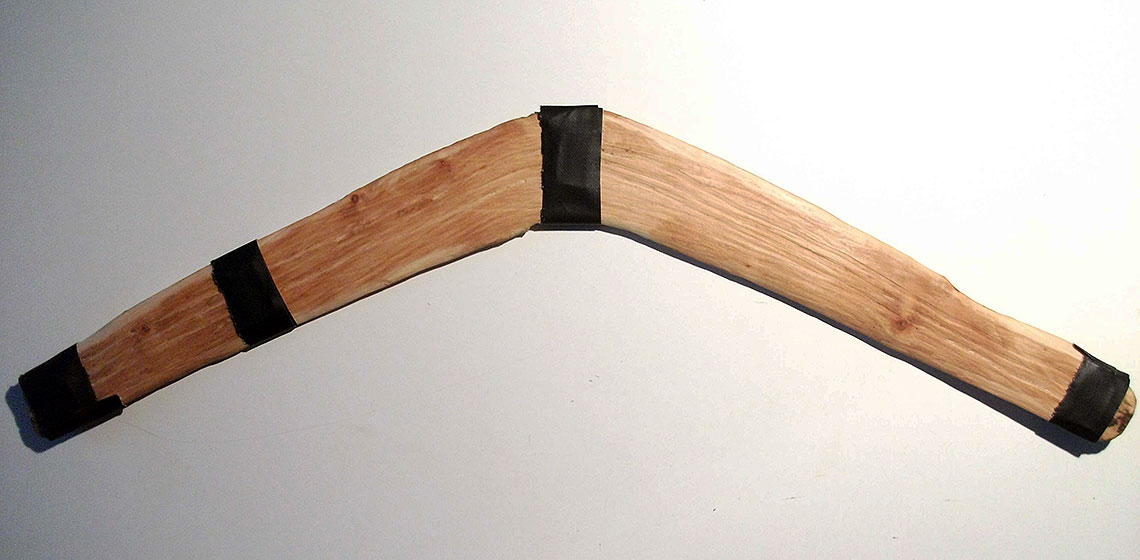
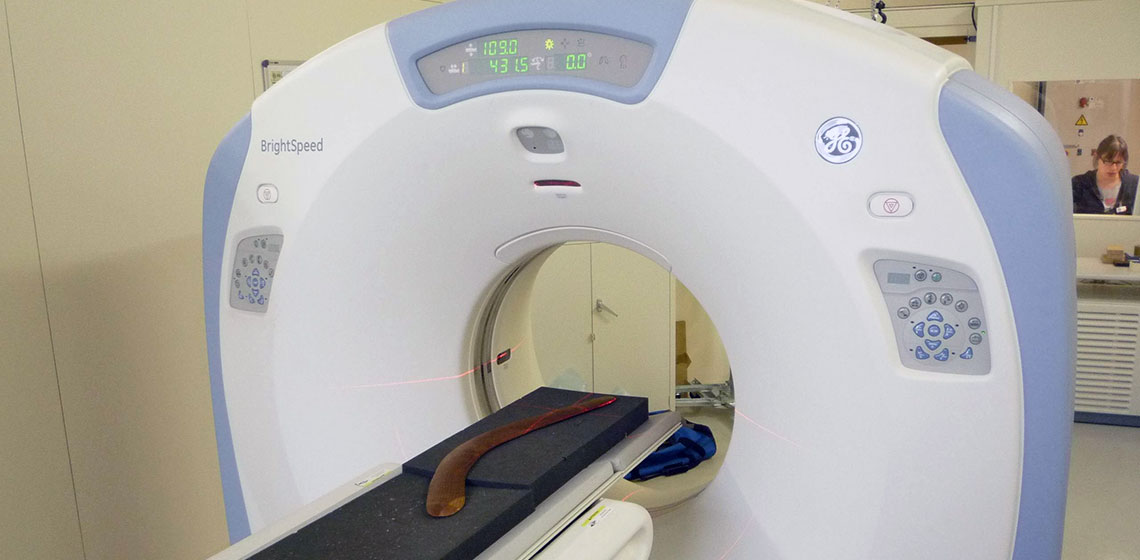
X-Ray Tomography and Infrared Spectrometry for the Analysis of Throwing Sticks & Boomerangs
Publication Date
In 2009, confronted to the study of throwing sticks collections from several museums and private collections (including more than three hundreds artefacts) and the need to evaluate their aerodynamic and functions, I developed a throwing stick classification and a methodology to measure their characteristics (Bordes, 2014). This approach is complementary to the gathering of ethnographic or archaeological contextual data to confirm or invalidate hypotheses about theirs functions.
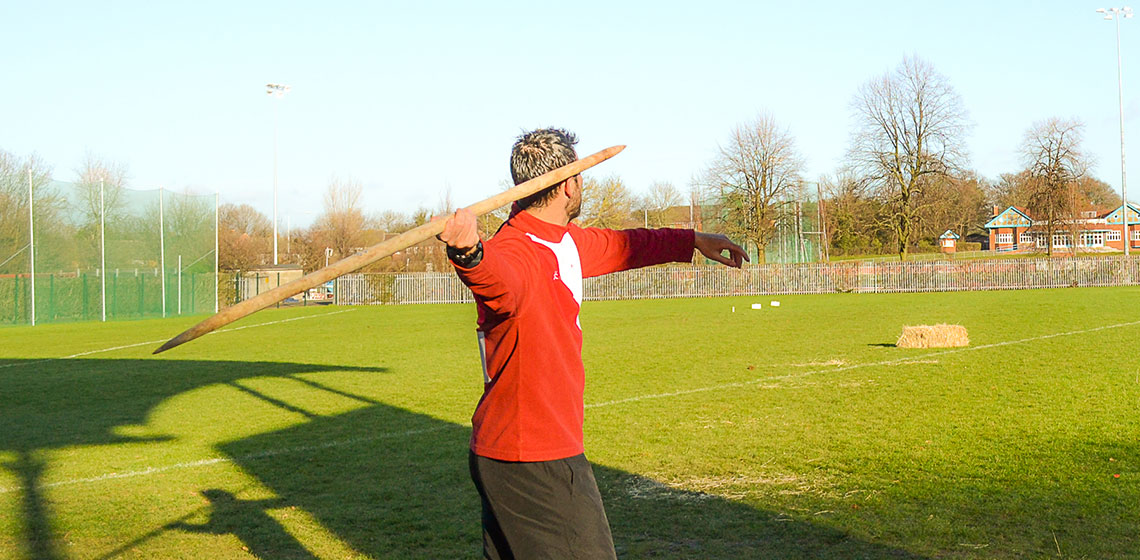
Skills Shortage: A Critical Evaluation of the Use of Human Participants in Early Spear Experiments
Publication Date
Hand-delivered spears are the earliest clear hunting technology in the archaeological record, with origins from 400,000 years ago, before the evolution of our own species. Experimental archaeological approaches to early weaponry continue to grow, and both controlled and naturalistic experiments are making significant contributions to interpreting such technologies...
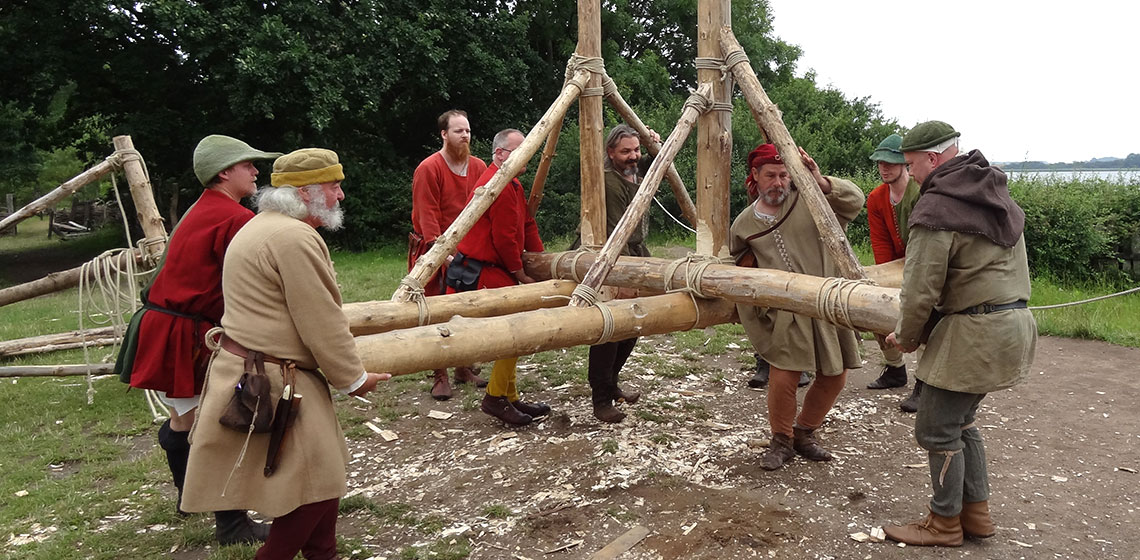
Traction Trebuchet
Publication Date
The trebuchet, in all its forms, was very much in vogue in the reenactment and research community in the 1980s and 1990s. Several museums around the world have also built their own, with Middelaldercenteret in Nykøbing Falster in Denmark as one of the first modern examples of counterweight trebuchet (Hansen, 1989). Despite the multitude of builds, very little has been published about...
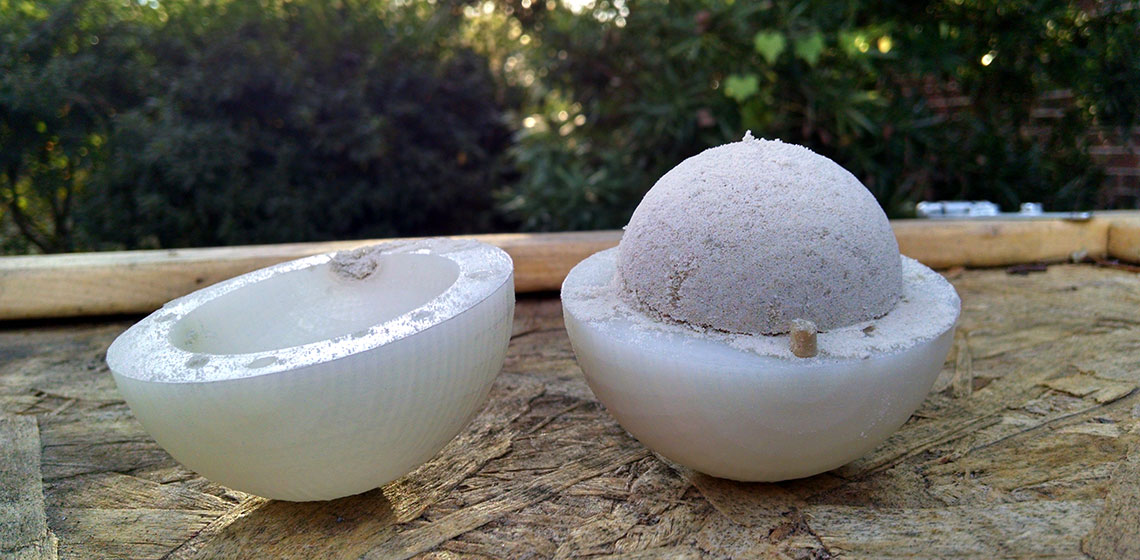
Shifting the Sand: Replicating Black Powder Grenades
Publication Date
Black powder hand grenades are ubiquitous for several European archaeological sites between 1600 AD and 1900 AD. Unfortunately, many archaeological reports only note the presence of hand grenades in artifact inventories, perhaps denoting some minor measurements. Only one report contains a full assessment of grenades, but this was performed by treasure hunters who excavated the pirate ship Whydah...
A Gaulish Throwing Stick Discovery in Normandy: Study and Throwing Experimentations
Publication Date
In 2010 archaeological excavations on the pre-Roman site of Urville Nacqueville, Normandy (France) discovered a shaped unknown wooden implement. This boomerang shaped wooden artefact, dated from 120 to 80 BC, has been found in an enclosure trench of a Gaulish village close to a ritual deposit of whalebones...
Stone Moulds from Terramare (Northern Italy): Analytical Approach and Experimental Reproduction
Publication Date
7th UK EA Conference Cardiff 2013
***A large number of stone moulds, dating to Middle and Late Bronze Age (approximately 1650-1150 BC) has been found in Terramare sites since the 19th century. They were made to produce a wide range of bronze objects, such as ornaments, weapons and tools. Empirical observations of casting experiments revealed that different types of stone do not give the same response to the heat of molten metal...
***A large number of stone moulds, dating to Middle and Late Bronze Age (approximately 1650-1150 BC) has been found in Terramare sites since the 19th century. They were made to produce a wide range of bronze objects, such as ornaments, weapons and tools. Empirical observations of casting experiments revealed that different types of stone do not give the same response to the heat of molten metal...